Guide to Muscle Building Supplements
Muscle building supplements are dietary products formulated to enhance muscle mass, improve strength, and support recovery. While proper nutrition and exercise are the foundations of muscle growth, certain supplements can support and enhance your efforts. This guide provides an in-depth look at the most effective supplements for muscle building, backed by scientific research and expert insights.
Key Factors for Muscle Growth
Before diving into supplements, it's crucial to understand the three main criteria for maximal muscle gain:
- Caloric surplus: Consuming more calories than you burn
- Adequate protein intake: Ingesting more protein than your body breaks down
- Progressive resistance training: Following a resistance based exercise program that stresses your muscles
While these criteria can be met without supplements, certain products may help you achieve your muscle-building goals more efficiently.
Overview of Muscle Building Supplements
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), approximately 20% of supplement users aim to enhance muscle mass. These supplements bridge nutritional gaps that may arise due to rigorous physical activity, ensuring optimal muscle growth and recovery. Creatine and protein supplements have the strongest evidence for effectiveness in muscle building. Other supplements may offer benefits for specific populations or under certain circumstances.
Importance of Supplements in Muscle Growth
Supplements, particularly protein, play a crucial role in promoting muscle hypertrophy and recovery. They offer concentrated nutrients that can be difficult to acquire through diet alone, especially during intense training periods. A systematic review by Pasiakos et al. (2015) highlights that protein supplementation can significantly enhance muscle mass and strength gains in conjunction with resistance training. This review emphasises that while untrained individuals may not see immediate benefits from protein supplementation early in their training, the combination of adequate training frequency, volume, and duration with protein intake can lead to substantial improvements in muscle hypertrophy and strength over time.
Additionally, the evidence suggests that protein supplements may also boost both aerobic and anaerobic performance. This synergy between proper nutritional support and exercise underscores the importance of strategic supplementation in maximizing muscle development and overall physical performance.
Key Benefits of Supplements:
- Nutrient Density: High concentrations of essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals.
- Enhanced Recovery: Reduced muscle soreness and accelerated repair.
- Performance Boost: Improved strength, endurance, and workout capacity.
However, it's crucial to understand that supplements are adjuncts to, not replacements for, a balanced diet and structured training program.
Prevalence of Supplement Use
Recent research provides insights into the prevalence and patterns of supplement use among regular gym-goers:
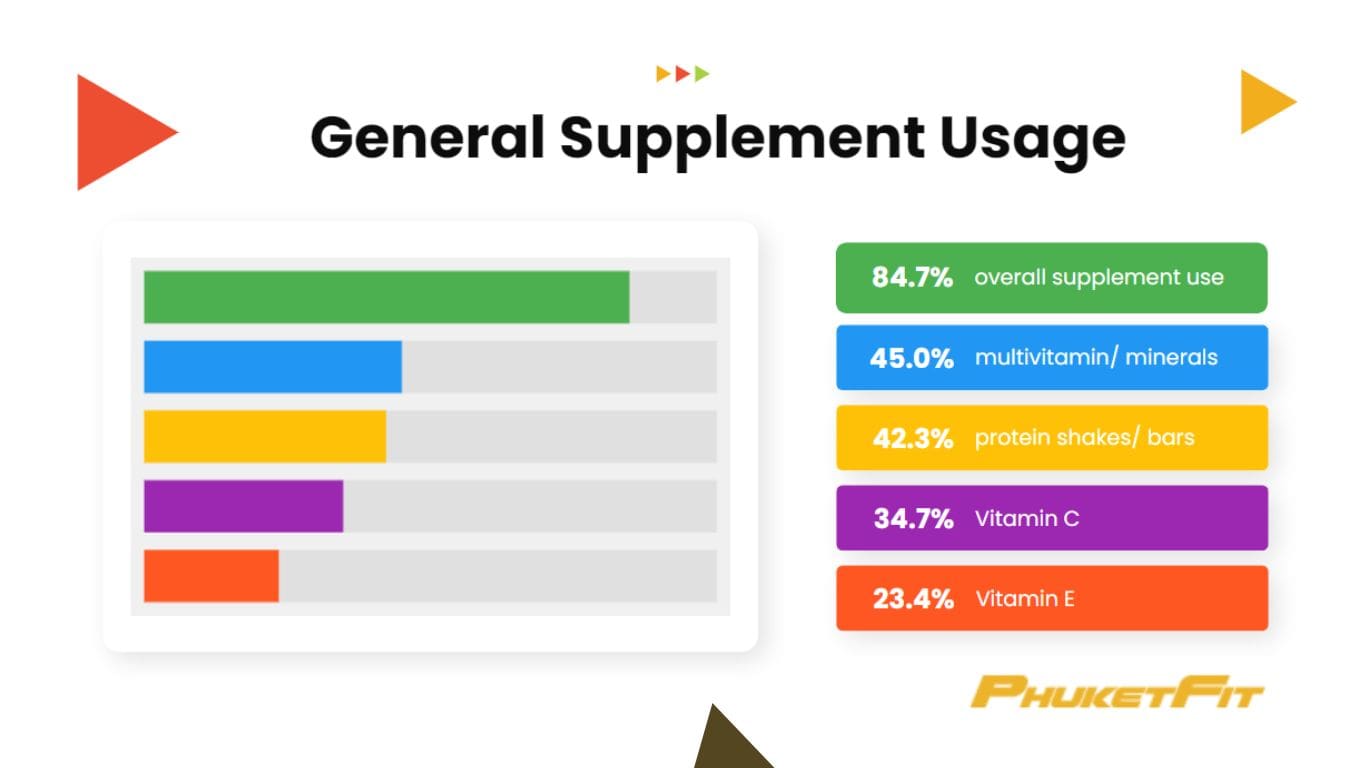
- A study conducted at a Long Island, NY gym found that 84.7% of participants used supplements (International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism).
- The most commonly used supplements at least 5 times per week were:
- Multivitamin/minerals (45%)
- Protein shakes/bars (42.3%)
- Vitamin C (34.7%)
- Vitamin E (23.4%)
Age-Related Differences in Supplement Use
Another study in the Southern Medical Journal 2004 revealed interesting age-related patterns in supplement choices and reasons for use:
- Participants over 45 were more likely to use multivitamins and vitamin E.
- Those 45 years or younger favoured protein supplements.
- Individuals under 30 consumed creatine more frequently.
- Older participants tended to take supplements to prevent future illness, while younger users focused on muscle building.
Impact of Exercise Goals on Supplement Use
The reasons for exercising influenced supplement choices:
- Bodybuilders more frequently consumed protein supplements, creatine, and ephedra compared to those exercising for general health reasons.
Key Supplements for Muscle Growth
Selecting scientifically validated supplements can optimise muscle-building efforts. Below, we examine key supplements supported by research.
Creatine
Creatine is one of the most extensively studied and effective supplements for increasing muscle mass and enhancing performance. Studies have shown that creatine supplementation can lead to significant gains in muscle size and strength. Here are the key points from a study from the International Society of Sports Nutrition:
Effectiveness and Mechanism:
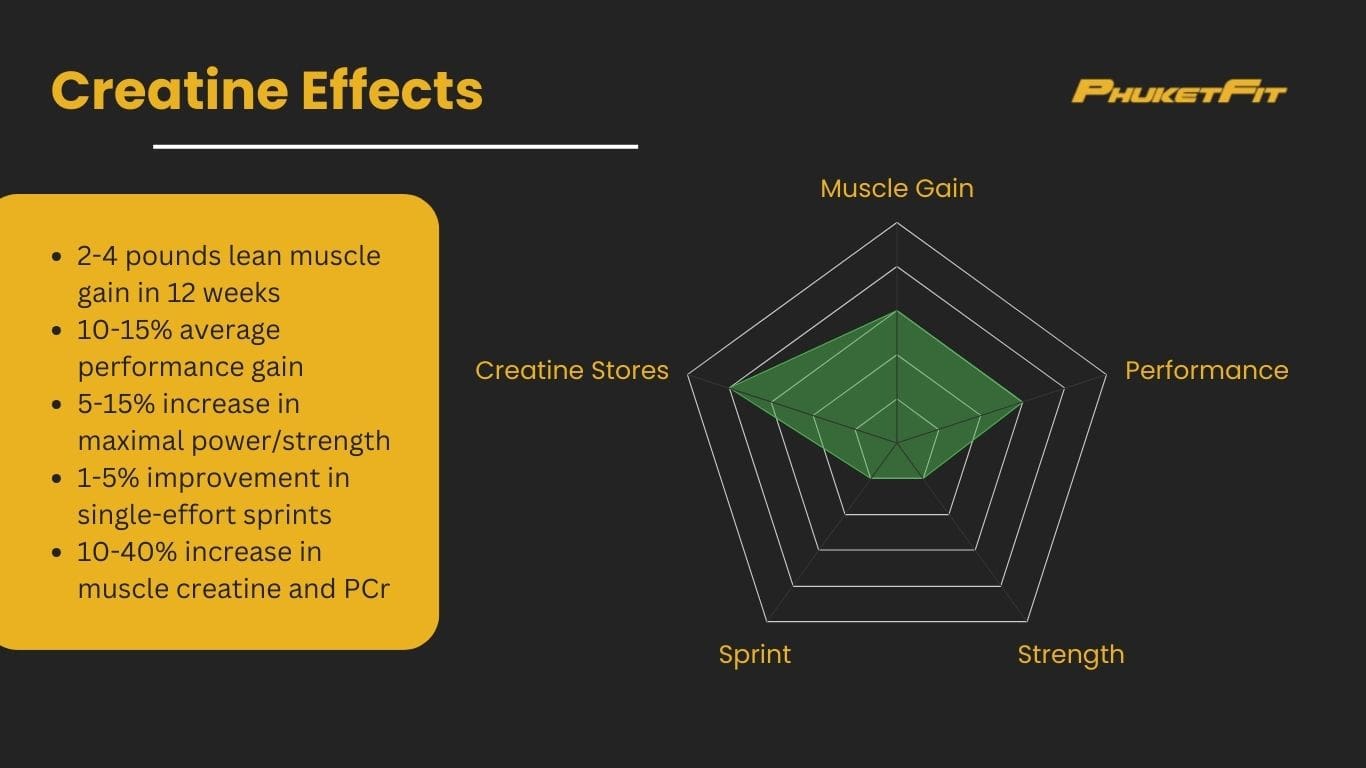
- Muscle Gain: Average of 2-4 pounds of lean muscle in 12 weeks
- Energy Production: Increased phosphocreatine stores for rapid ATP production
- Training Capacity: Allows for increased workload during resistance training
Performance Improvements
- Overall: 10-15% average gain in performance metrics
- Specific Gains:
- 5-15% increase in maximal power/strength
- 5-15% increase in work during maximal effort sets
- 1-5% improvement in single-effort sprints
- 5-15% increase in repetitive sprint performance
Physiological Changes
- Creatine Stores: 10-40% increase in muscle creatine and PCr
- Body Composition:
- 1-2 kg increase in first week
- 2-4 pounds extra muscle over 4-12 weeks
- Long-term Adaptations: 5-15% greater strength and performance gains with training
Additional Benefits
- Increased muscle fiber size and protein synthesis
- Enhanced glycogen storage
- Improved recovery and reduced muscle damage
Note: Individual results may vary based on factors like initial creatine levels, exercise type, and diet.
Safety Profile:
- Studies of up to 5 years show no adverse effects in healthy individuals and confirm creatine's safety and efficacy for both males and females, with no significant adverse effects when used appropriately.
Dosage Recommendations:
- Loading Phase: 20 grams per day (divided into 4 doses) for 5-7 days.
- Maintenance Phase: 3-5 grams per day thereafter.
How Does Creatine Supplementation Compare to Other Muscle-Building Supplements?
Creatine is considered superior to many other supplements due to its extensive research support and proven efficacy. It works by increasing phosphocreatine stores in muscles, thereby improving high-intensity exercise performance.
Protein Supplements
Protein supplements, particularly whey protein, are fundamental for muscle repair and growth.
Role in Muscle Synthesis:
- Amino Acid Provision: Provides essential amino acids that stimulate muscle protein synthesis, with free-form EAA ingestion rapidly increasing peripheral EAA concentrations, enhancing muscle maintenance and performance even without exercise (International society of sports nutrition, 2023).
- Enhanced Recovery: Facilitates repair of muscle fibres damaged during exercise.
Efficacy:
- Increased Lean Mass: Consuming 20-40 grams of whey protein post-exercise has been shown to significantly increase lean body mass and strength (Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 2017).
- Dietary Support: Particularly beneficial for individuals unable to meet protein needs through diet alone.
Types of Protein Supplements:
- Whey Protein Isolate: High protein content with minimal fats and lactose.
- Casein Protein: Slow-digesting, ideal for sustained amino acid release.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Options like pea or soy protein for vegetarians and vegans.
Are There Any Side Effects of Taking Whey Protein Powder Regularly?
Regular consumption of whey protein powder is generally safe for most individuals. However, excessive intake may lead to digestive issues like bloating or cramping in some people. A review in HealthCare (2024) highlights that whey protein is generally well-tolerated; however, individuals with lactose intolerance should consider whey protein isolate or other alternative protein sources to avoid adverse effects.
Beta-Alanine
Beta-alanine is a non-essential amino acid that enhances performance by buffering muscle acidity.
Mechanism and Benefits:
- Carnosine Production: A research conducted by Dunnett & Harris in 2009 says Carnosine increases intramuscular levels, buffering hydrogen ions and delaying muscle fatigue. It is synthesised from β-alanine and L-histidine (Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition).
- Performance Enhancement: May improve high-intensity exercise capacity and endurance.
Effectiveness on Muscle Mass:
- Mixed Evidence: While some studies show performance benefits, the impact on muscle hypertrophy is less clear. Research from 2022 says Beta-alanine supplementation showed no effect on body mass, fat mass, body fat percentage, or fat-free mass (International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health).
Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)
BCAAs consist of leucine, isoleucine, and valine, crucial for muscle protein synthesis.
Key Points:
- Leucine's Role: A research published in J Anim Sci (2010), this study highlights how leucine stimulates protein synthesis in neonatal pigs by activating the mTORC1 pathway, increasing phosphorylation of S6K1 and 4EBP1. While leucine promotes muscle protein synthesis, this effect is short-lived, as the stimulation depends on the availability of all essential amino acids.
- Supplementation Outcomes: A 2017 study published in Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition concluded that the claim of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) stimulating muscle protein synthesis in humans is unsupported, as evidence shows they may actually decrease protein synthesis and breakdown, and a separate study in Frontiers in Physiology found no significant benefits of BCAAs over adequate dietary protein intake.
Considerations:
- Dietary Protein Sufficiency: For individuals consuming sufficient high-quality protein, additional BCAAs may offer limited benefits.
- Potential Uses: May aid those with inadequate protein intake or during prolonged exercise when muscle catabolism is a concern.
Beta-Hydroxy Beta-Methyl butyrate (HMB)
HMB is a metabolite of leucine believed to reduce muscle protein breakdown.
Research Insights:
- Muscle Damage Reduction: A research published on Sports Med in 2008 says exercise-induced muscle damage (EIMD) can impair muscle function and performance, but interventions like long-term antioxidant and protein supplementation have shown effectiveness in reducing its negative effects, while high-dose NSAIDs are discouraged due to their impact on muscle adaptation; prior eccentric exercise also provides protective benefits, highlighting the need for further research on optimal intervention strategies and evidence-based guidelines.
- Effectiveness Debate: A research from The International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN) in 2013 asserts that beta-hydroxy-beta-methyl butyrate (HMB) can enhance recovery and skeletal muscle hypertrophy, strength, and power in both trained and untrained individuals, particularly when consumed close to workouts and for a duration of two weeks prior to exercise, with a recommended daily dose of 38 mg per kg of body mass, while highlighting that HMB is safe for both young and older populations.
Usage Recommendations:
- Dosage: Typically 3 grams per day.
- Target Population: Beginners or those returning from injury may experience greater benefits.
Weight Gainers
Weight gainers are high-calorie supplements designed for individuals struggling to consume enough calories for muscle growth.
Composition and Purpose:
- Macronutrient Mix: Often contains a ratio of carbohydrates to protein (e.g., 3:1) to provide energy and building blocks for muscle.
- Caloric Density: Can provide over 1,000 calories per serving.
Effectiveness:
- Not a Standalone Solution: Must be combined with resistance training; excess calories without training can lead to fat gain (International Journal of Exercise Sciences, 2017).
Considerations:
- Nutrient Quality: Choose products with quality ingredients and minimal added sugars.
- Individual Needs: Assess whether whole foods can meet caloric needs before relying on supplements.
Understanding gender-specific responses to supplements is crucial, particularly for female athletes seeking optimised results.
Female-Specific Considerations
Women may experience different physiological responses to certain supplements due to hormonal differences and metabolism.
Creatine and Female Athletes
Creatine's Impact on Women:
- Metabolic Differences: Women may have lower baseline creatinine stores, potentially making supplementation more impactful (Nutrients, 2021).
- Performance Benefits: Research from Nutrients in 2021 indicates that women typically have 70–80% lower endogenous creatine stores than men, making creatine supplementation potentially more impactful for them, especially during critical life stages such as menses, pregnancy, postpartum, and post-menopause, as well as for athletes as it may improve strength, exercise performance, skeletal muscle size, and cognitive function, while high doses of 0.3 g·kg−1·d−1 can yield significant benefits, particularly when combined with resistance training.
Safety and Dosage:
- Well-Tolerated: No significant adverse effects reported in women.
- Standard Dosage: Similar to men; may adjust based on body weight.
Protein Needs for Women
Age and Protein Requirements:
- Increased Needs with Age: Research in the Environmental Research and Public Health in 2022 indicates that older women may require higher protein intake to counteract sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss).
- Anabolic Resistance: Older adults experience anabolic resistance, requiring higher protein doses (around 1.2 g/kg/d or more) to effectively stimulate muscle protein synthesis compared to younger individuals. (Frontiers in Nutrition, 2021).
Recommendations:
- Protein Timing and Distribution: Consuming 25-30 grams of protein per meal may optimise muscle protein synthesis.
- Quality Sources: Emphasise high-quality proteins rich in essential amino acids.
Exploring additional supplements can provide further support for muscle growth and overall performance.
Additional Supplements to Consider
Beyond the primary supplements, others may offer ancillary benefits for muscle development and recovery.
Glutamine
Role in the Body:
- Amino Acid Abundance: Most abundant amino acid in plasma and skeletal muscle.
- Immune Function: Glutamine is crucial for immune function, supporting immune cells and potentially aiding recovery during intense training and catabolic states. (Nutrients, 2018).
Effectiveness for Muscle Growth:
- Limited Impact: A 2019 meta-analysis in Clinical Nutrition concluded that glutamine supplementation had no significant impact on athletic performance, muscle mass, or immune function, though it was associated with weight reduction.
- Situational Use: May benefit those with glutamine depletion due to overtraining or illness.
Collagen
Benefits for Joint and Muscle Health:
- Connective Tissue Support: Provides amino acids for collagen synthesis in joints and tendons.
- Recovery Aid: Research in the Springer Link (2021) showed improved joint pain and degenerative bones in athletes supplementing with collagen.
Muscle Mass Implications:
- Potential Synergy: A 2015 study in the Cambridge Open Access found that collagen peptide supplementation alongside resistance training significantly improved body composition and muscle strength in elderly men, suggesting a potential synergy in enhancing muscle mass in older adults.
L-Carnitine
Function and Potential Benefits:
- Fat Metabolism: Facilitates the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production.
- Recovery and Performance: l-Carnitine supplementation has been shown to improve exercise recovery by reducing muscle injury and soreness while enhancing energy metabolism, although a 2018 meta-analysis from Nutrients reported mixed results regarding its effectiveness on muscle soreness and recovery.
Efficacy for Muscle Growth:
- Inconclusive Evidence: More research is needed to confirm its benefits for muscle hypertrophy.
Testosterone Boosters
Purpose and Use Cases:
- Hormonal Support: Aimed at increasing testosterone levels, which can influence muscle mass.
- Target Population: May benefit individuals with clinically low testosterone.
Effectiveness and Safety:
- Mixed Results: A 2020 study from The World Journal of Men's Health found that while 90% of "testosterone boosting" supplements claimed to enhance testosterone levels, only 24.8% had supporting evidence, highlighting concerns over their efficacy and safety due to often exceeding recommended doses of vitamins and minerals.
- Potential Risks: Hormonal supplements can have side effects; professional consultation is advised.
Implementing best practices ensures that supplementation effectively contributes to muscle-building goals.
Best Practices for Supplementation
Optimizing the benefits of supplements involves strategic integration with diet and training.
Combining Supplements with Diet
Holistic Nutrition Approach:
- Primary Nutrition from Whole Foods: A research from The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics in 2013 advocates for a total diet approach to healthy eating, emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet with whole foods and moderation, rather than labelling specific foods as good or bad.
- Supplementation as an Adjunct: Use supplements to address specific deficiencies or increased demands.
Macronutrient Balance:
- Protein: 1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight per day for muscle growth (Nutrients, 2018).
- Carbohydrates and Fats: Adequate intake supports energy needs and hormonal function.
Importance of Resistance Training
Essential Role in Muscle Growth:
- Stimulus for Hypertrophy: Muscle growth necessitates mechanical tension achieved through resistance exercises, which is essential for inducing hypertrophy and enhancing muscle strength (Sports Medicine, 2023).
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increasing training intensity promotes continuous adaptation.
Supplementation Synergy:
- Timing Matters: Consuming protein supplements around training sessions can enhance muscle protein synthesis.
- Consistency is Key: Regular training combined with proper nutrition yields the best results.
In conclusion, understanding individual needs and evidence-based supplement use is crucial for achieving muscle-building objectives.
Conclusion
Selecting the right supplements depends on individual needs, goals, and scientific evidence supporting their efficacy. While many supplements can aid muscle growth, it is essential to:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Obtain personalized advice to ensure safety and appropriateness.
- Integrate with Diet and Training: Use supplements to complement, not replace, a balanced diet and consistent resistance training.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of the latest research to make evidence-based decisions.
Alternative Considerations:
- Sleep and Recovery: Priorities adequate rest to support muscle repair.
- Stress Management: High stress can impede muscle growth; incorporate relaxation techniques.
- Hydration: Essential for overall performance and nutrient delivery.
By adopting a comprehensive approach that includes evidence-based supplementation, balanced nutrition, and effective training strategies, individuals can optimize their muscle-building efforts and achieve their fitness goals.